The law of supply and demand is an economic theory that explains how buyers and sellers interact to determine the price and supply of a resource. The theory explores the impacts of availability and demand for products and services.
We can apply the law of supply and demand to all types of goods, from fresh produce to ASX shares.
What is the law of supply?
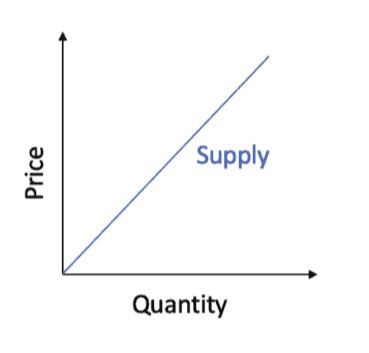
The law of supply says suppliers will produce more of a good if it sells at higher prices. This makes sense, as higher prices mean increased revenue. Suppliers are willing to deliver more products and services when paid more for doing so.
The law of supply can be graphed via the supply curve, which shows the correlation between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied for a given period.
What is the law of demand?
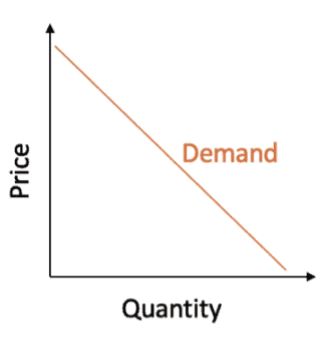
The law of demand says that there will be demand for a higher quantity of a particular product as its price reduces. This is because consumers can afford to buy more if prices are lower.
Conversely, the higher the price, the lower the demand. This is because the opportunity cost of purchasing a particular good increases with the price. The law of demand can be graphed via the demand curve, which shows the correlation between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded in a given period.
How does the law of supply and demand work?
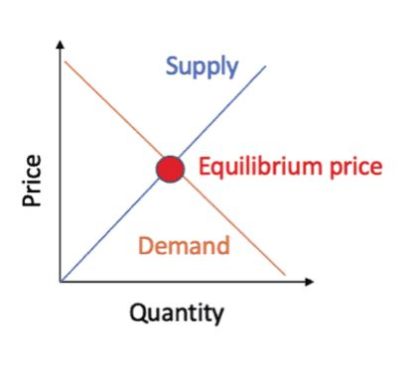
The law of supply and demand says that the price and quantity of a particular good will be determined by the point at which the supply curve and demand curve intersect. At this point, consumers are willing to buy the same quantity of goods as sellers are willing to produce. This is the equilibrium quantity.
At this point, the market-clearing price is known as the 'equilibrium price'. Suppliers can sell all the units they wish to supply at the equilibrium price, and buyers can buy all the units they want.
What factors impact demand?
Numerous factors can impact the level of demand for different goods and services. This shifts the demand curve, changing market equilibrium. Total demand depends on the quantity of a product consumers are willing and able to purchase at a particular price.
Consumer preference impacts demand – if we do not want or need something, we are unlikely to buy it. Consumer preference can be influenced by advertising and publicity, brand awareness, and perceived value.
Our ability to buy products is a function of our income and expenses. Therefore, as personal incomes increase, we see demand rise. Excess demand will result in an upward shift in prices.
The price of related and complementary goods can also impact demand. If you are a buyer shopping for a new car, you may compare similar models from different manufacturers. The price of one model will affect how much you are willing to pay for another.
When goods are complementary, a change in the price or demand for one affects the other. For example, a decrease in the price of video game consoles may increase consumer demand for video games. This, in turn, can cause a price increase.
Factors impacting supply
The supply level is impacted by factors that encourage or discourage production. The availability of workers, weather, technology, and government subsidies can all cause a shift in the supply curve.
Where the price of inputs or the cost of production falls, producers can supply more goods at a lower price. Similarly, improvements in productivity and investments in capacity can increase supply.
Supply can be constrained by factors such as bad weather, which can cause agricultural yields to fall, and higher taxes, which increase the cost of goods. A supply shock is an unexpected event that suddenly changes the supply of a product. Issues in the supply chain can impact producers, causing the market price of a good to rise.
Why is the law of supply and demand important?
By understanding the law of supply and demand, we can better understand the factors impacting the price and availability of resources. This can help us predict future demand and future supply. We can determine the quantity of goods producers will need to supply at a given price.
The law of supply and demand also applies to the share market. The price of an ASX share is the equilibrium price of the supply curve and demand curve at the time the share is sold.
Share prices fluctuate as a result of changes in supply and demand. When a company reports good news, the share price can shift upwards. Sellers may demand a higher price for their shares, and buyers may be more willing to pay that price. Conversely, if there is a deterioration in a company's outlook, a downward price change can occur. Buyers may offer less for shares, and the equilibrium point shifts down.

